Canada Gazette, Part I, Volume 156, Number 24: Carriages and Strollers Regulations
June 11, 2022
Statutory authority
Canada Consumer Product Safety Act
Sponsoring department
Department of Health
REGULATORY IMPACT ANALYSIS STATEMENT
(This statement is not part of the Regulations.)
Executive summary
Issues: The requirements of the Carriages and Strollers Regulations (Regulations) have not changed substantively since they were introduced in 1985, while carriage and stroller design has evolved considerably. Current designs of carriages and strollers may present hazards that are not addressed by the Regulations. In addition, some terminology could be clarified and updated to keep pace with current designs. Health Canada has also identified requirements that are not aligned with the requirements in other jurisdictions, and the limited time provided to transition from one standard or regulation to a new version, to be issues warranting amendment.
Description: Health Canada is proposing to repeal and replace the Regulations to address these issues by (a) aligning mechanical requirements with those in other jurisdictions through ambulatory incorporation by reference of international standards, including a period during which stakeholders may meet the mechanical requirements of either the previous or new version of an international standard; (b) aligning surface coating materials requirements with the proposed amendments to the Surface Coating Materials Regulations that were prepublished in the Canada Gazette, Part I, on April 24, 2021; (c) aligning toxicological requirements with the Toys Regulations; (d) aligning phthalates requirements with the Phthalates Regulations; (e) increasing alignment of information and warning requirements with other jurisdictions, and maintaining the official languages requirement for all information and warnings to be written in both English and French.
Rationale: This regulatory proposal is expected to help reduce the number of injuries in children by adding mechanical, information, and warning requirements to address known hazards that arose after the current Regulations came into force, including strangulation, entrapment, and the integrity of car seat attachments. This regulatory proposal will also help prevent harmful health effects in children by addressing phthalates hazards in carriages and strollers. There are no expected safety benefits from the changes to the toxicological and surface coating materials requirements, the proposed changes are intended to update and clarify the terminology regarding toxicological and surface coating materials requirements. This regulatory proposal is expected to generate monetary benefits primarily through a reduction in costs to industry. Every company sampled during the cost-benefit analysis survey identified that some cost savings would occur as a result of not having to test to multiple mechanical standards when supplying the North American market because of the proposed Regulations’ alignment with international standards. A cost-benefit analysis of this proposal for the 11-year period from 2023 to 2033 estimates annualized net benefits of approximately $1.1 million.
Issues
This regulatory proposal addresses five types of requirements for carriages and strollers:
- Mechanical requirements
- Surface coating materials requirements
- Toxicological requirements
- Phthalates requirements
- Information and warnings requirements
The following sections outline issues with each type of requirement addressed by this regulatory proposal.
Mechanical requirements
Health Canada has identified the following issues with the mechanical requirements of the current Carriages and Strollers Regulations (Regulations):
- Current designs of carriages and strollers may present hazards that are not addressed by the Regulations, such as the fall hazard posed by the detachment of a car seat accessory or wheel from a product.
- The requirements of the Regulations are not aligned with the requirements in other jurisdictions, such as the United States.
- The terminology in some areas of the Regulations require updating to keep pace with current technology and designs. For example, Schedule 1 to the Regulations uses the terms “parcel rack” and “parcel bag,” which have fallen out of common use and have become ambiguous.
Surface coating materials requirements
The current Regulations incorporate by reference the requirements in section 23 of the Toys Regulations, which describe requirements for a “surface coating material that is applied to a toy.” The wording of the Regulations could be specific to the surface coating material applied to carriage and strollers.
Toxicological requirements
The current Regulations incorporate by reference the requirements in section 22 and section 25 of the Toys Regulations, which describe toxicological requirements for toys. The wording of the Regulations could be specific to toxicological hazards in carriages and strollers.
Phthalates requirements
The current Regulations do not include phthalates requirements nor are carriages and strollers within the scope of the Phthalates Regulations. Parts of a carriage or stroller made of vinyl containing certain phthalate plasticizers would present the same hazards as are addressed by the Phthalates Regulations.
Information and warning requirements
Current designs of carriages and strollers may present hazards that are not addressed by the information and warning requirements of the current Regulations. Additionally, the information and warning requirements are not aligned with those in other jurisdictions.
Background
Carriages and strollers are wheeled vehicles designed to transport infants and children. The Regulations were introduced in 1985 under Part II of Schedule I to the Hazardous Products Act (HPA) to help protect the health and safety of infants and children. The Regulations include design, performance, and labelling requirements intended to minimize or eliminate hazards associated with carriages and strollers.
On June 20, 2011, the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA) came into force and replaced Part I and Schedule I to the HPA. All consumer product safety regulations under the HPA were transferred under the CCPSA. In 2016, the Regulations were amended to remove any references to the HPA. The amendments also addressed several housekeeping revisions to reflect changes to legislative drafting practices, and to correct English and French inconsistencies. The requirements of the Regulations were not changed substantively in 2016.
Current designs of carriages and strollers may present hazards that were not accounted for in 1985 and are not addressed by the current Regulations. As part of ongoing efforts to review the existing suite of regulations under the CCPSA, opportunities to modernize the Regulations with the proposed amendments were identified to help improve health and safety and increase regulatory alignment with other jurisdictions.
The proposed Regulations include documents incorporated by ambulatory reference, using the words “as amended from time to time.” This means that any future change to those documents will become part of the Regulations. As a document is changed, the new version would become part of the regulation without needing to amend the Regulations.
Objective
The objectives of this regulatory proposal are to repeal and replace the current Regulations
- to improve health and safety by addressing hazards that arose after the Regulations came into force in 1985;
- to align with the mechanical requirements in other jurisdictions, through ambulatory incorporation by reference of international standards, where appropriate;
- to maintain alignment of surface coating materials requirements with other Canadian regulations;
- to maintain alignment of toxicological requirements with other Canadian regulations;
- to align phthalates requirements with other Canadian regulations;
- to update and clarify the terminology of the Regulations; and
- to implement periods after new versions of international standards are published during which products can meet either the new or the previous version of the standard.
This proposal links to Government of Canada regulatory reform initiatives to address health and safety considerations while helping to reduce the compliance burden on industry and improving the alignment of requirements with other jurisdictions.
Description
This regulatory proposal covers five types of requirements related to carriages and strollers:
- Mechanical
- Surface coating materials
- Toxicological
- Phthalates
- Information and warnings
The following sections summarize the proposed requirements.
Proposed Amendments to Mechanical Requirements
Health Canada is proposing to address the mechanical hazards related to current designs of carriages and strollers by aligning Canadian requirements with international requirements, where appropriate. Health Canada proposes to align with the mechanical requirements of both ASTM International, ASTM F833, Standard Consumer Safety Performance Specification for Carriages and Strollers (ASTM F833) and International Organization for Standardization, ISO 31110, Wheeled child conveyances — Pushchairs and prams - Requirements and test methods (ISO 31110). Health Canada reviewed the requirements of these standards and determined that they adequately address the mechanical hazards related to current designs of carriages and strollers.
Health Canada proposes that alignment can be achieved by requiring compliance with:
- the requirements from ASTM F833 excluding those set out in sections 5.3, 5.12, 8 and 9, incorporated by ambulatory reference; or
- the requirements from ISO 31110 excluding those set out in sections 6, 7 and 10, incorporated by ambulatory reference, and in addition, the entrapment requirements from ASTM F833 sections 6.8 and 6.10.
The sections of ASTM F833 and ISO 31110 that have been excluded from incorporation by reference are addressed by other sections of the proposed Regulations, or by other Canadian legislation.
The proposed Regulations include a period when a new version of a standard incorporated by reference is published that would allow 180 days to manufacture or import and 365 days to advertise or sell products that meet either the new or the previous version of the standard. The longer period to advertise or sell products is provided because future changes to incorporated standards will not go through the Canada Gazette publication process, so stakeholders will have less time to prepare in advance of the changes. Furthermore, future changes to these two standards are expected to be incremental, so the risk to consumers from continuing to advertise and sell products compliant to the previous version of either of these standards is expected to be low.
The following list outlines Health Canada’s proposed amendments to the mechanical requirements of the Regulations, the hazards they address, and the relevant sections in the current Regulations, ASTM F833 and ISO 31110. This list is set out in the order these sections appear in the ASTM F833 standard.
- Product and accessory definitions: Introduce and update terminology to account for new designs of carriages, strollers, and accessories and to align with other jurisdictions, where appropriate. This change relates to section 1 of the current Regulations, section 3 of ASTM F833, and section 3 of ISO 31110.
- Sharp parts and surfaces: Amend the requirements and test method for sharp edges, corners, points, projections, burrs, and cracks and for smooth finish. This change relates to section 10 of the current Regulations, sections 5.1, 5.4, and 5.10 of ASTM F833, and section 8.7 of ISO 31110.
- Small parts choking hazard: Amend the requirements and test method for small parts by adding the torque test method to test for the removal of protective components. This change relates to section 11 of the current Regulations, sections 5.2 and 5.10 of ASTM F833, and section 8.5 of ISO 31110.
- Latching system integrity: Amend the requirements and test method to evaluate the structural integrity of the latching mechanisms. This change relates to section 7 of the current Regulations, section 5.5 of ASTM F833, and section 8.3.5 of ISO 31110.
- Open holes: Amend the requirements and test method for open holes (holes or slots). This change relates to section 12 of the current Regulations, section 5.6 of ASTM F833, and section 8.2 of ISO 31110.
- Scissoring, shearing and pinching: Amend the dimensions specified in the requirements and clarify the test method for addressing folding carriages and strollers. This change relates to section 3 of the current Regulations, section 5.7 of ASTM F833, and section 8.3 of ISO 31110.
- Exposed coil springs: Introduce a more specific requirement and test method to address exposed coil springs accessible to the occupant. This change relates to section 12 of the current Regulations, section 5.8 of ASTM F833, and section 8.2.1 of ISO 31110.
- Information permanency: Amend the requirements and test method to evaluate permanency of safety information and warnings. This change relates to section 14 of the current Regulations, section 5.9 of ASTM F833, and section 9 of ISO 31110.
- Strangulation and entanglement: Introduce a length requirement to address the strangulation hazard from cords and straps. This change relates to section 5.13 of ASTM F833 and section 8.4 of ISO 31110.
- Parking brake: Amend the requirements and test method for evaluating the parking brake system. This change relates to section 5 of the current Regulations, section 6.1 of ASTM F833, and section 8.8 of ISO 31110.
- Structural integrity: Amend the requirements and test method to evaluate structural integrity. Car seat accessories that comply with the requirements of the Motor Vehicle Restraint Systems and Booster Seats Safety Regulations will be excluded. This section relates to sections 8 and 13 of the current Regulations, section 6.2 of ASTM F833, and section 8.10 of ISO 31110.
- Stability: Amend the requirements and test method to evaluate stability for strollers with an adjustable back rest to test them in the most reclined position in addition to the most upright position. Also adding requirements and a test method for the stability of carriages and strollers with accessories. This change relates to section 4 of the current Regulations, section 6.3 of ASTM F833, and section 8.9 of ISO 31110.
- Restraining system integrity: Amend the requirements and test method and introduce requirements and a test method for buckle release and carriage accessories. This change relates to section 6 of the current Regulations, section 6.4 of ASTM F833, and section 8.1.3 of ISO 31110.
- Occupant retention: Introduce requirements and a test method to evaluate the ability of a carriage or stroller to retain the occupant. This change relates to section 6.5 of ASTM F833 and section 8.1.1 and 8.1.2 of ISO 31110.
- Car seats and other accessories: Introduce requirements and a test method to evaluate the attachment of accessories to the frame of carriages and strollers. Amend various requirements to account for designs with accessories. This change relates to section 6.6 of ASTM F833 and section 8.10 of ISO 31110.
- Impact: Introduce requirements and a test method to evaluate the continuing performance of carriages and strollers following an impact. This change relates to section 6.7 of ASTM F833 and sections 8.10.4 and 8.10.5 of ISO 31110.
- Entrapment: Introduce requirements and a test method to evaluate head entrapment beneath a tray or a grab bar, and entrapment in openings such as the foot opening. This change relates to sections 6.8 and 6.10 of ASTM F833.
- Wheel integrity: Introduce requirements and a test method to assess the attachment of the wheels to the axle. Also introduce requirements and a test method for a secondary retention device for removable wheel fork assembly designs. This change relates to section 6.9 of ASTM F833 and section 8.10.6 of ISO 31110.
- Suffocation: Introduce requirements addressing the suffocation hazard for internal lining of carriage bodies, and for the flexible film bags used to package carriages or strollers. This change relates to section 8.6 of ISO 31110.
- Structural integrity of carrying handles: Introduce requirements and test methods addressing the structural integrity of carrying handles for carriage bodies or seat bodies with carrying handles. This change relates to section 8.10.1 of ISO 31110.
- Stability of carriage body: Introduce requirements and a test method for the maximum angle of inclination for a carriage body suspended from its carrying handle. This change relates to section 8.10.2 of ISO 31110.
- Handle strength: Introduce requirements and test methods for the integrity of carriage or stroller handles. This change relates to section 8.10.7 of ISO 31110.
Proposed Amendments to Surface Coating Materials Requirements
The current Regulations refer to the requirements for surface coating materials set out in section 23 of the Toys Regulations. A regulatory amendment to the Surface Coating Materials Regulations that included a subsequent amendment to section 23 of the Toys Regulations was prepublished in the Canada Gazette, Part I, on April 24, 2021. The amendment to section 23 of the Toys Regulations would make those requirements consistent with the proposed Surface Coating Materials Regulations.
To increase clarity, Health Canada is proposing to remove the reference to the Toys Regulations and include requirements consistent with the proposed Surface Coating Materials Regulations directly in the text of the proposed Regulations.
Proposed Amendments to Toxicological Requirements
The current Regulations refer to toxicological requirements set out in sections 22 and 25 of the Toys Regulations. Health Canada is proposing to maintain these requirements by including them directly into the text of the proposed Regulations. These requirements allow for existing median lethal dose and median lethal concentration data to be used, such that no animal testing is required.
Proposed Amendments to Phthalates Requirements
The current Regulations do not include requirements addressing phthalates content, and carriages and strollers are not within the scope of the Phthalates Regulations. Health Canada is proposing to add requirements addressing phthalates content by including requirements consistent with the Phthalates Regulations directly in the text of the proposed Regulations.
Proposed Amendments to Information and Warning Requirements
The content of the proposed information and warning requirements also exist in either ASTM F833 or ISO 31110, and many requirements exist in both standards. However, information and warnings that meet ASTM F833 or ISO 31110 are not necessarily compliant with the proposed regulations due to the requirement for text to be presented in both French and English. To allow flexibility in wording, the proposed information and warning requirements do not specify the exact wording required to comply and allow industry the option to compose wording that may meet the requirements of multiple jurisdictions. The proposed formatting requirements align with the formatting requirements of both ASTM F833 and ISO 31110.
The proposed Regulations include requirements for
- information that must be printed on carriages or strollers;
- information that may be printed on carriages or strollers or that may accompany them;
- information that must be printed on packaging;
- warnings that must be printed on carriages and strollers;
- warnings that may be printed on carriages or strollers or that may accompany them; and
- warnings that must be printed on packaging.
Proposed Transitional Provision and Coming-into-Force
The proposed Regulations come into force on the day on which they are published in the Canada Gazette, Part II. These proposed Regulations include a transitional provision that allows a product compliant to the current Regulations to continue to be manufactured, imported, advertised, or sold in Canada for 180 days beginning on the day the proposed Regulations come into force.
Regulatory development
Consultation
In spring 2021, Health Canada conducted a pre-Canada Gazette, Part I, consultation on proposed amendments to the Regulations. The consultation was published online for 45 days, from May 3, 2021, to June 17, 2021. A total of 11 responses were received, six from manufacturers, one from a manufacturing association, one from a retailer, one from a retailer association, one from a consumer, and one from a product testing laboratory.
The consultation responses included strong support for incorporating mechanical requirements from ASTM F833 by ambulatory reference. The responses did not present opposition to also incorporating mechanical requirements from ISO 31110 to provide the option of complying with either standard.
The public consultation proposed a 180-day transition period after publication of a new version of a standard incorporated by reference for manufacturing, import, advertisement and sale. During this period, products could comply with either the new version of the standard, or the previous version. At the end of the period, all products would have to comply with the new version of the standard. Nearly all (10 of 11) respondents voiced concerns that 180 days would not be sufficient time to meet a new version of a standard. The main concern raised by stakeholders was that 180 days would not be sufficient time for existing products to be sold. This regulatory proposal maintains the 180-day transition period for manufacture and import that was proposed during the public consultation. In response to stakeholder concerns, the proposal was changed to include a 365-day transition period for advertisement and sale after the publication of a new version of a standard incorporated by ambulatory reference.
One manufacturer and one manufacturing association requested that the requirements to limit phthalate content apply only to accessible vinyl parts of carriages and strollers. Health Canada is proposing to maintain alignment of phthalates requirements with those found in the Phthalates Regulations. Accordingly, the proposed requirements addressing diisononyl phthalate (DINP), diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP) and di-n-octyl phthalate (DNOP) apply only to parts of a carriage or stroller that can, in a reasonably foreseeable manner, be placed in the mouth of a child under four years, and those addressing di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) apply to all vinyl parts of a carriage or stroller.
The response from a consumer expressed concerns regarding the lack of requirements for certain elements and for perfluorooctanoic acids and other fire retardants in vinyl or cloth coverings. These substances are not addressed in either the existing Regulations or the proposed Regulations. Assessments of certain flame retardants and their possible risks to human health and the environment are ongoing under the Government of Canada’s Chemicals Management Plan. Where a chemical is found harmful to human health, appropriate risk management actions would be considered to help protect the health or safety of the public.
Modern treaty obligations and Indigenous engagement and consultation
In accordance with the Cabinet Directive on the Federal Approach to Modern Treaty Implementation, an initial assessment was conducted on this regulatory proposal. The assessment concluded that implementation of this proposal would be unlikely to impact on the rights, interests or self-government provisions of treaty partners. All people of Canada, including Indigenous peoples, would benefit from this proposal.
Instrument choice
Health Canada considered the following options:
- Maintain status quo — Health Canada would continue to monitor the compliance of carriages and strollers to the Carriages and Strollers Regulations, and take corrective actions when necessary. If this option were to be selected, the general prohibitions in sections 7 and 8 of the CCPSA may be used to address mechanical hazards related to designs associated with carriages and strollers that emerged after 1985. The general prohibitions may also be used to address hazards from phthalates in vinyl parts of carriages and strollers. However, industry has indicated that regulations provide more clarity compared to the general prohibitions. The Department would continue to provide industry with information about their obligations under the CCPSA and its regulations.
- Certain requirements and test methods in the current Regulations are not clearly defined in how they apply to more recent designs, resulting in frequent inquiries from stakeholders requesting interpretation.
- Therefore, due to the issues of clarity discussed above, maintaining status quo is not the preferred option.
- Amend the Carriages and Strollers Regulations by drafting mechanical requirements directly in the Regulations. This option would address hazards that arose after the Regulations came into force in 1985, incorporate the mechanical requirements from other jurisdictions by drafting the requirements into the Regulations, and align phthalates requirements, toxicological requirements, and surface coating materials requirements with other Canadian regulations. Drafting the mechanical requirements into the Regulations enables Health Canada to control all future amendments to these requirements, and to update and clarify the terminology of the Regulations.
- This is not the preferred option because it would require repeated regulatory amendments to remain aligned with other jurisdictions as their mechanical requirements change over time.
- Amend the Carriages and Strollers Regulations by incorporating mechanical requirements from international standards via ambulatory reference. The preferred option is to amend existing regulatory requirements. The proposed amendments would address hazards that arose after the Regulations came into force in 1985, incorporate the mechanical requirements from other jurisdictions by ambulatory reference, and align phthalates requirements, toxicological requirements, and surface coating materials requirements with other Canadian regulations. Ambulatory incorporation by reference enables the Regulations to remain aligned with other jurisdictions as the mechanical requirements change over time. The proposed amendments would also update and clarify the terminology of the Regulations, and implement periods after new requirements come into force during which stakeholders may meet either the previous or new requirements.
- This option was chosen because clear and consistent regulatory requirements help regulated parties comply and also help Health Canada take quick corrective action in the event of non-compliance, which helps protect the health and safety of Canadians.
Regulatory analysis
Benefits and costs
In 2020, Health Canada retained Cheminfo Services Inc. of Markham, Ontario, to analyze the costs and benefits associated with this regulatory proposal. The cost-benefit analysis (CBA) report is available upon request from the contact listed at the end of this Regulatory Impact Analysis Statement.
Costs
As part of the CBA, a survey of carriage and stroller manufacturers, brand owners, and importers was undertaken. The survey ultimately resulted in inputs from eleven companies. It is estimated that these respondents cover approximately two thirds of all carriages and strollers sold in Canada. The major findings were as follows:
- All of the manufacturers and brand owners responding to the survey indicated that there would be no incremental cost increases resulting from the proposed mechanical amendments.
- Only one company indicated that there would be additional costs from the proposed phthalate requirements. That company indicated the incremental cost of testing to the proposed phthalates requirements would be less than $400 per year. For the purposes of this analysis, the annual costs from the phthalates requirements is extrapolated to be about $1,000 per year, based on the costs to that company and the survey market coverage.
- Inputs from manufacturers suggest that a transition period of at least 180 days would be required to allow manufacturers to sell their inventories of products compliant to the previous requirements. Some inventories of products compliant to the previous requirements may remain in the hands of wholesalers and retailers after the 180-day transition period passes. No data are available to quantify or monetize the extent to which inventories of products compliant to the previous requirements would exist at the wholesale or retail level after a 180-day transition period. The proposed Regulations increased the transition period for advertisement and sale to 365 days to decrease the amount of products remaining at retail that are non-compliant to the new requirements.
The impact of information and warning requirements was not quantified in the CBA. The impact is expected to be small because all proposed information and warning requirements already exist in either ASTM F833 or ISO 31110, and many exist in both standards.
Health Canada estimates that purchasing or modifying test equipment would have a one-time cost to government of $150,000 in 2021 dollars. This proposal assumes no ongoing costs to the Government, because the costs to administer, promote and enforce the proposed Regulations would be integrated as part of Health Canada’s existing compliance and enforcement program for consumer products. This integration would not significantly change current practices.
Benefits
This regulatory proposal is expected to generate benefits primarily through a reduction in costs to industry members. Every company contacted during the CBA identified that some cost savings would occur as a result of not having to test to multiple mechanical standards when supplying the North American market. Cost savings identified by the sampled companies ranged from a low of $200 to well over $100,000 per company. These cost savings were then translated to cost savings per carriage or stroller sold by each company.
The estimated cost savings per carriage or stroller sold by each company ranged from a low of about $0.20 to a high of over $15.00. The high-end response from a company was described as including the test costs avoided and also the benefits of enabling the sharing of the same parts across platforms, and not having to design and manufacture parts specific to Canada. These types of consolidations generate minimum order savings from suppliers and other supply chain efficiencies.
This regulatory proposal is also likely to generate benefits by reducing the adverse health effects to Canadians caused by incidents involving carriages and strollers. Information available from the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission indicates that between 7,000 and 14,000 emergency room visits occur in the U.S. annually as a result of the use of carriages and strollers. In Canada, comprehensive estimates of the number of injuries arising from use of carriages and strollers do not exist. Pro-rating the U.S. results suggests that up to about 1,500 emergency room visits may occur in Canada annually, with 75% of these by children under the age of five. The Public Health Agency of Canada reports that an average of 255 carriage or stroller-related head injuries occur per year in Canada, and 170 of these involve traumatic brain injury. The extent that injuries would be reduced by this regulatory proposal was not quantified because incident data includes limited details on the pathways to injury. Injuries related to behaviour and the way the products are used, rather than design features, may not be addressed by this regulatory proposal.
Cost-benefit analysis
This analysis estimates that about 200,000 strollers were sold in Canada in 2021. The annual sale of strollers is assumed to increase at a rate of 0.75% per year, consistent with the increase in the annual number of live births between 2000 and 2019.
An accounting statement for the 11-year period from 2023 to 2033 is shown in Table 1 below, using a central scenario of $6.00 cost savings per carriage or stroller. The statement shows annualized net benefits of approximately $1.1 million.
- Number of years: 12 (2022 to 2033)
- Base year for costing: 2021
- Present value base year: 2022
- Discount rate: 7%
| Impacted stakeholder | Description of cost | 2023 | 2024 | 2033 | Total (present value) |
Annualized value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Capital | $150,000 | $0 | $0 | $131,016 | $16,495 |
| Industry | Testing to phthalates requirements | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $7,008 | $882 |
| All stakeholders | Total costs | $151,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $138,024 | $17,377 |
| Impacted stakeholder | Description of benefit | 2023 | 2024 | 2033 | Total (present value) |
Annualized value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industry | Decreased testing, minimum order savings | $1,218,068 | $1,227,203 | $1,312,568 | $8,819,422 | $1,110,383 |
| All stakeholders | Total benefits | $1,218,068 | $1,227,203 | $1,312,568 | $8,819,422 | $1,110,383 |
| Impacts | 2023 | 2024 | 2033 | Total (present value) | Annualized value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total costs | $151,000 | $1,000 | $1,312,568 | $138,024 | $17,377 |
| Total benefits | $1,218,068 | $1,227,203 | $1,312,568 | $8,819,422 | $1,110,383 |
| Net Impact | $1,067,068 | $1,226,203 | $1,311,568 | $8,681,398 | $1,093,005 |
Note: The annualized value calculation is based on 2022 being t=1, the number of periods n=12, and a discount rate of 7%.
Small business lens
A number of small businesses were included in the CBA survey. The two Canadian small carriage and stroller manufacturers (that have the products manufactured outside of Canada) did not identify that the regulatory proposal would have differential impacts on them.
In general, the unit costs of carriage and stroller testing are higher from smaller manufacturers. For example, a company that pays $1,000 for testing per year across 1,000 carriages and strollers pays a higher unit cost than a company that pays $1,000 for testing per year across 10,000 carriages and strollers. As the regulatory proposal is expected to reduce mechanical testing costs, the proposal is benefiting small businesses.
The proposed Regulations include a transitional provision that allows a carriage or stroller compliant to the current Regulations to continue to be manufactured, imported, advertised, or sold in Canada for 180 days beginning on the day the proposed Regulations come into force. This will help mitigate costs for all sizes of business, including small businesses, by providing time for existing inventory to be sold.
One-for-one rule
This regulatory proposal does not affect the administrative burden on businesses, as there are no associated reporting or record-keeping requirements. Health Canada is not proposing new or incremental requirements to demonstrate compliance, including collecting, processing, reporting or retaining information. The proposed Regulations would not change the administrative costs on industry; therefore, this proposal complies with the one-for-one rule.
Regulatory cooperation and alignment
This proposal is not part of an existing formal regulatory cooperation initiative, because the United States Consumer Product Safety Commission is not subject to the Canada–United States Regulatory Cooperation Council. However, the proposal is in line with the Regulatory Cooperation Council’s objectives to increase regulatory alignment between the two countries while maintaining high levels of protection for health and safety.
The proposed mechanical requirements increase alignment with other jurisdictions, by providing the option to meet the mechanical requirements from either ASTM F833 or ISO 31110. This would increase alignment with the United States, because they incorporate ASTM F833 in their final rule, 16 CFR part 1227 – Safety Standard for Carriages and Strollers, by ambulatory reference. Health Canada is not aware of any jurisdictions that currently require compliance to the ISO 31110 standard, which was published for the first time in December 2020. It is likely that other jurisdictions may adopt this standard in the future. The committee that maintains the ISO 31110 standard includes stakeholders from the broadest range of jurisdictions of any standard for carriages and strollers, including members from the European Union, the United States, China, the United Kingdom, Japan and Australia. Manufacturers design primarily for other markets and then modify their products for the Canadian market if needed. Alignment of Canadian mechanical requirements with those of other jurisdictions would reduce the need for design modifications for Canada.
The proposed surface coating materials, toxicological, and phthalates requirements maintain or increase alignment with other Canadian regulations. The proposed surface coating materials requirements maintain alignment with the proposed Surface Coating Materials Regulations. The proposed toxicological requirements maintain alignment with the Toys Regulations. The proposed phthalates requirements increase alignment with the Phthalates Regulations.
The current information and warning requirements do not align with other jurisdictions. The content of the proposed information and warning requirements also exist in either ASTM F833 or ISO 31110, and many requirements exist in both standards. However, information and warnings that meet ASTM F833 or ISO 31110 are not necessarily compliant with the proposed regulations due to the requirement for text to be presented in both French and English. To allow flexibility in wording, these proposed requirements do not specify the exact wording required to comply and allow industry the option to compose wording that may meet the requirements of multiple jurisdictions. The formatting requirements align with the formatting requirements of both ASTM F833 and ISO 31110. Therefore, it is not expected that the information and warning requirements will increase the burden on industry.
Strategic environmental assessment
In accordance with the Cabinet Directive on the Environmental Assessment of Policy, Plan and Program Proposals, a preliminary scan concluded that a strategic environmental assessment is not required.
Gender-based analysis plus
The Canadian Hospitals Injury Reporting and Prevention Program found 1,239 carriage and stroller-related injuries reported between April 1, 2011, and July 17, 2017, in children less than five years old. For injuries that were not traumatic brain injuries, males represented 54.3% of cases. Infants and one-year-olds accounted for the majority (69.6%) of cases. The Public Health Agency of Canada’s report Injury in Review 2020 Edition: Spotlight on Traumatic Brain Injuries Across the Life Course found that carriages and strollers are one of the nursery products most frequently associated with injuries. It found 1,081 carriage- and stroller-related traumatic brain injuries reported between April 1, 2011, and July 17, 2017, by the Canadian Hospitals Injury Reporting and Prevention Program. Males represented 52.8% of traumatic brain injuries. The report also found that between 1990 and 2010, in the United States National Electronic Injury Surveillance System, an estimated 12,470 carriage and stroller-related injuries were treated each year.
This regulatory proposal is expected to help reduce the number of injuries in children by adding mechanical requirements to address known hazards that arose after the current Carriages and Strollers Regulations came into force, including strangulation, entrapment, and car seat attachments. However, the expected reduction cannot be quantified because incident data includes limited details on the pathways to injury of reported incidents.
According to the Phthalates Regulations Regulatory Impact Analysis Statement published in 2010, the Phthalates Regulations were enacted because a product composed, in whole or in part, of soft vinyl containing certain phthalate plasticizers has the potential to cause harmful health effects in young children that suck or chew on the soft vinyl for prolonged periods of time. Carriages and strollers are not within the scope of the Phthalates Regulations, and the current Regulations do not include phthalates requirements. However, if made of vinyl containing certain phthalate plasticizers, parts of a carriage or stroller would present the same hazards as are addressed by the Phthalates Regulations.
This regulatory proposal is expected to benefit children by reducing their potential exposure to phthalate plasticizers. However, data are not available to quantify the potential impact of the phthalates requirements. A survey performed for the cost-benefit analysis of this regulatory proposal found that most manufacturers thought carriages and strollers were already required to comply with the Phthalates Regulations. Therefore, the impact of the phthalates requirements is expected to be small, as it is unlikely these hazards are present in many carriages or strollers currently available in Canada.
Implementation, compliance and enforcement, and service standards
The regulatory proposal would be made under the authority of the CCPSA, and would come into force on the day on which it is published in the Canada Gazette, Part II. These proposed Regulations include a transitional provision that allows a product compliant to the current Regulations to continue to be manufactured, imported, advertised, or sold in Canada for 180 days beginning on the day the proposed Regulations come into force. During this time, regulated parties may comply with either the previous Regulations or the proposed Regulations.
The proposed Regulations include a period when a new version of a standard incorporated by reference is published that would allow 180 days to manufacture or import and 365 days to advertise or sell products that meet either the new or the previous version of the standard.
Health Canada would develop information materials to help industry stakeholders understand and comply with the amended requirements. The test methods used by Health Canada’s Product Safety Laboratory will be made available upon request to the Government of Canada.
Compliance and enforcement activities would follow established Health Canada approaches and procedures, including sampling and testing of products, inspections at business locations, follow-up on incidents reported by the Canadian public and public health organizations, and follow-up on mandatory incident reports by industry. Non-compliant products would be subject to the enforcement actions available to Health Canada inspectors under the CCPSA, and may include voluntary commitment to product correction by industry, negotiation with industry for the voluntary removal of non-compliant products from the market, seizure, orders for recall or other measures, administrative monetary penalties or prosecution.
Contact
Veronica Carpani
Consumer and Hazardous Products Safety Directorate
Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch
Department of Health
Address locator: 4908B
269 Laurier Avenue West
Ottawa, Ontario
K1A 0K9
Fax: 613‑952‑2551
Email: CCPSA-LCSPC@hc-sc.gc.ca
PROPOSED REGULATORY TEXT
Notice is given that the Governor in Council, pursuant to section 37footnote a of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act footnote b, proposes to make the annexed Carriages and Strollers Regulations.
Interested persons may make representations concerning the proposed Regulations within 70 days after the date of publication of this notice. All such representations must cite the Canada Gazette, Part I, and the date of publication of this notice, and be addressed to Veronica Carpani, Senior Regulatory Policy and Risk Management Advisor, Consumer and Hazardous Products Safety Directorate, Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch, Department of Health, Mail Stop: 4908B, 269 Laurier Avenue West, Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0K9 (email: CCPSA-LCSPC@hc-sc.gc.ca)
Ottawa, June 2, 2022
Wendy Nixon
Assistant Clerk of the Privy Council
Carriages and Strollers Regulations
Definitions
Definitions
1 The following definitions apply in these Regulations.
- accessible part
- for the purposes of section 5, means any part of a product that may be touched, licked, mouthed or swallowed during the reasonably foreseeable use of the product. (partie accessible)
- ASTM F833
- means the ASTM F833 standard entitled Standard Consumer Safety Performance Specification for Carriages and Strollers, published by ASTM International, as amended from time to time. (norme ASTM F833)
- carriage
- means a wheeled vehicle that is designed to transport a child in a reclined or horizontal position, and includes a wheeled vehicle that is designed to be converted to function as a carriage and has been so converted. (landau)
- good laboratory practices
- means practices that are in accordance with the principles set out in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development document entitled OECD Principles of Good Laboratory Practice, Number 1 of the OECD Series on Principles of Good Laboratory Practice and Compliance Monitoring, ENV/MC/CHEM(98)17, the English version of which is dated January 21, 1998 and the French version of which is dated March 6, 1998. (bonnes pratiques de laboratoire)
- good scientific practices
- means
- (a) in the case of test data, conditions and procedures that are in accordance with or equivalent to those set out in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development document entitled OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, as amended from time to time; and
- (b) in the case of laboratory practices, good laboratory practices. (bonnes pratiques scientifiques)
- ISO 31110
- means the ISO 31110 standard entitled Wheeled child conveyances — Pushchairs and prams — Requirements and test methods, published by the International Organization for Standardization, as amended from time to time. (ISO 31110)
- LC50
- means the concentration of a substance in air that, when administered by means of inhalation over a specified length of time in an animal assay, is expected to cause the death of at least 50% of a defined population of animals. (CL50)
- LD50
- means the single dose of a substance that, when administered by a defined route in an animal assay, is expected to cause the death of at least 50% of a defined population of animals. (DL50)
- stroller
- means a wheeled vehicle that is designed to transport a child in a seated position and includes a wheeled vehicle that is designed to be converted to function as a stroller and has been so converted. (poussette)
- surface coating material
- for the purposes of section 5, means a paint or other similar material, with or without pigment, that forms a solid film after it is applied to a surface and that can be removed. (revêtement)
Technical Requirements
Requirements — standards
2 (1) Carriages and strollers must meet either:
- (a) the requirements set out in ASTM F833, except sections 5.3, 5.12, 8 and 9 of that standard; or
- (b) the requirements set out in sections 6.8 and 6.10 of ASTM F833 and those set out in ISO 31110, except sections 6, 7 and 10 of ISO 31110.
Compliance period
(2) Despite subsection (1), a carriage or stroller that meets the requirements set out in either paragraph (1)(a) or (b) as the requirements read on the day before the day on which a new version of ASTM F833 or ISO 31110, as the case may be, is published may continue to meet those requirements for the following activities
- (a) in the case of the manufacture or import of a carriage or stroller, for the period of 180 days that begins on the day on which the new version of the applicable standard is published; and
- (b) in the case of the advertising or sale of a carriage or stroller, for the period of 365 days that begins on the day on which the new version of the applicable standard is published.
Prohibited substances
3 A carriage or stroller must not contain any of the following substances if the substance could, under reasonably foreseeable circumstances, become accessible to a child or, if the substance is used as a filling, could be released on breakage or leakage:
- (a) carbon tetrachloride or any substance that contains it;
- (b) any substance that contains more than 10 mg of methyl alcohol per gram;
- (c) any substance that contains more than 100 mg of petroleum distillates per gram;
- (d) benzene;
- (e) any substance that contains more than 100 mg of turpentine per gram;
- (f) boric acid or salts of boric acid;
- (g) ethyl ether.
Toxic substances
4 If a carriage or stroller contains a toxic substance, at least one of the following requirements must be met:
- (a) the substance must not be capable of being ingested, inhaled or absorbed through the skin because of the nature, physical form, size or any other characteristic of the carriage or stroller;
- (b) the total quantity of the substance for a child who has a body weight of 10 kg must not exceed the lesser of
- (i) 1% of the oral LD50 as determined in accordance with good scientific practices, and
- (ii) 1% of the dermal LD50 as determined in accordance with good scientific practices;
- (c) the toxicity of the substance must not exceed the limits set out in Schedule 1.
Specific substances in surface coatings
5 A sticker, film or other similar material that can be removed, or a surface coating material, that is applied to an accessible part of a carriage or stroller must not contain, when it is tested in accordance with a method that conforms to good laboratory practices,
- (a) more than 90 mg/kg total lead;
- (b) any compound of antimony, arsenic, cadmium, selenium or barium if more than 1000 mg/kg of the compound migrates from the material; or
- (c) more than 10 mg/kg total mercury.
Phthalates — DEHP, DBP and BBP
6 The vinyl in a carriage or stroller must not contain more than 1000 mg/kg of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP) or benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) when tested in accordance with a method that conforms to good laboratory practices.
Phthalates — DINP, DIDP and DNOP
7 (1) The vinyl in any part of a carriage or stroller that can, in a reasonably foreseeable manner, be placed in the mouth of a child under four years of age must not contain more than 1000 mg/kg of diisononyl phthalate (DINP), diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP) or di-n-octyl phthalate (DNOP) when tested in accordance with a method that conforms to good laboratory practices.
Interpretation
(2) For the purpose of subsection (1), a part of a carriage or stroller can be placed in the mouth of a child under four years of age if
- (a) it can be brought to the child’s mouth and kept there so that it can be sucked or chewed; and
- (b) one of its dimensions is less than 5 cm.
Dimensions — deflated state
(3) For the purpose of paragraph (2)(b), if a part of a carriage or stroller is inflatable, its dimensions must be determined in its deflated state.
Information
Presentation of Information
Languages and legibility
8 The information required by these Regulations must
- (a) be displayed in both English and French; and
- (b) be legible and clearly displayed, including being printed in characters whose colour contrasts sharply with the background.
9 (1) The information required by these Regulations must be printed in a standard sans-serif type that
- (a) is not compressed, expanded or decorative;
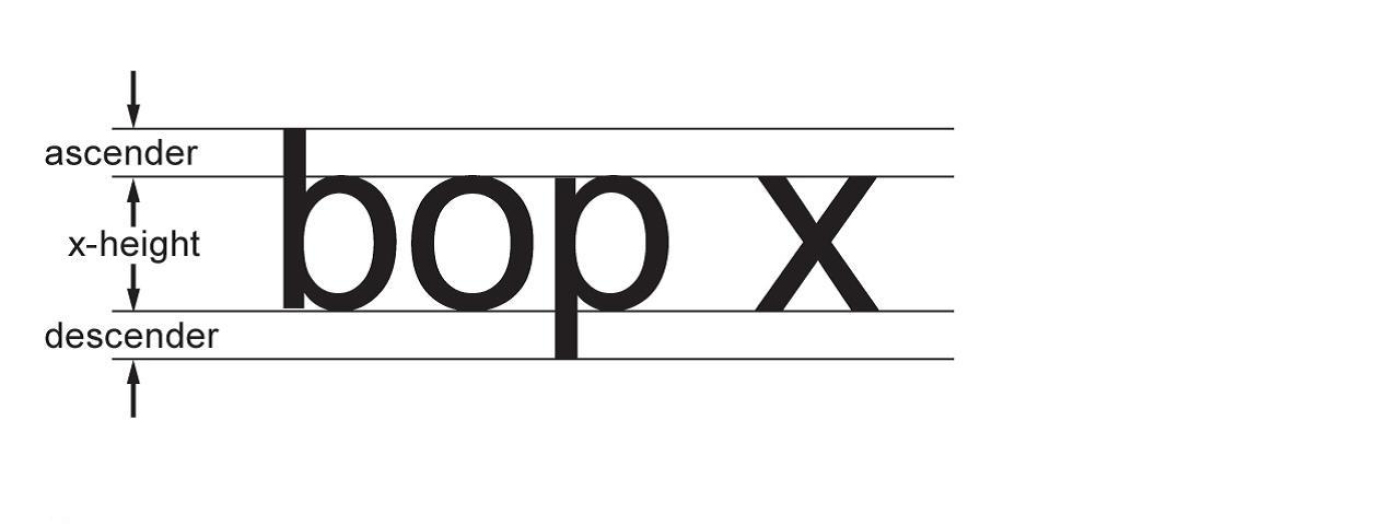
- (b) has a large x-height relative to the ascender or descender of the type, as illustrated in Schedule 2; and
- (c) has a height of not less than 2.5 mm.
Height of type
(2) The height of the type is determined by measuring an upper-case letter or a lower-case letter that has an ascender or a descender, such as “b” or “p”.
Signal words
10 The signal words “WARNING” and “MISE EN GARDE” must be displayed in upper-case type.
Required Information
Reference to Canada Consumer Product Safety Act or Regulations
11 Information that appears on a carriage or stroller, that accompanies a carriage or stroller or that is in any advertisement for a carriage or stroller must not make any direct or indirect reference to the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act or these Regulations.
Information — general
12 (1) The following information must be permanently printed on every carriage or stroller, or on a label that is permanently affixed to it:
- (a) in the case of a carriage or stroller that is manufactured in Canada, the name and principal place of business of the manufacturer or the person for which the carriage or stroller was manufactured;
- (b) in the case of a carriage or stroller that is imported for commercial purposes, the name and principal place of business of the manufacturer, the person for whom the carriage or stroller was manufactured or the importer;
- (c) the model name or model number of the carriage or stroller; and
- (d) the year and month of manufacture of the carriage or stroller.
Additional information
(2) Every carriage or stroller must display or be accompanied by the following information, with line drawings or photographs illustrating the sequence of steps if needed:
- (a) If it is sold not fully assembled, how it is to be assembled;
- (b) how it is to be folded and unfolded, if it is capable of being folded;
- (c) the manufacturer’s recommended maximum weight of the child;
- (d) the manufacturer’s recommended use positions;
- (e) how the braking device is to be operated;
- (f) how the child restraint system is to be used;
- (g) in the case of carriages or strollers with an integral or added part that is intended to carry a load, the details of the maximum permissible load;
- (h) how it is to be maintained and cleaned; and
- (i) any other information for safe usage.
Warning — general
13 The following warning, or its equivalent, must be permanently printed on every carriage or stroller, or on a label that is permanently affixed to it:
WARNING
- Never leave the child unattended.
- Avoid serious injury from falling or sliding out. Always use the child restraint system.
MISE EN GARDE
- Ne jamais laisser l’enfant sans surveillance.
- Des blessures graves peuvent survenir si l’enfant tombe ou glisse du siège. Toujours utiliser le système de retenue.
Warning and instructions — removable wheel
14 In the case of a carriage or stroller with a removable wheel-fork assembly, the following must be permanently printed on the wheel fork, or on a label that is permanently affixed to it:
- (a) the following warning or its equivalent:
WARNING
- Fall Hazard. Wheel can detach and cause tip over.
MISE EN GARDE
- Risque de chute. Le landau ou la poussette risque de basculer si la roue amovible se détache.
- (b) information that states how to verify that the wheel is securely attached.
Warning — foam
15 In the case of a carriage or stroller with a removable cover placed over foam on a tray or grab bar, the following warning, or its equivalent, must be permanently printed on the foam, or on a label that is permanently affixed to it:
WARNING
- Choking hazard. Only use with cover installed.
MISE EN GARDE
- Risque d’étouffement. Utiliser seulement lorsque le recouvrement est installé.
Warning — precaution
16 Every carriage or stroller must display or be accompanied by the following warning or its equivalent:
WARNING
- To avoid injuries from finger entrapment, ensure that the child is kept away when unfolding and folding this product.
- The carriage or stroller will become unstable if the manufacturer’s recommended load is exceeded.
MISE EN GARDE
- Pour éviter toute blessure aux doigts, tenir l’enfant à l’écart lors du repliage et du dépliage.
- Tout poids supérieur à la limite recommandée par le fabricant rendra le landau ou la poussette instable.
Information — container
17 (1) The following information must be permanently printed on a container in which a carriage or stroller is sold to a consumer, or on a label that is permanently affixed to the container:
- (a) in the case of a carriage or stroller that is manufactured in Canada, the name and principal place of business of the manufacturer or the person for which the carriage or stroller was manufactured;
- (b) in the case of a carriage or stroller that is imported for commercial purposes, the name and principal place of business of the manufacturer, the person for which the carriage or stroller was manufactured or the importer;
- (c) the model name or model number of the carriage or stroller; and
- (d) the year and month of manufacture of the carriage or stroller.
Warning — container
(2) A flexible film bag that contains a carriage or stroller or that is in the container must meet at least one of the following requirements:
- (a) it must have an opening of less than 356 mm in circumference;
- (b) it must be made from film that is at least 0.019 mm thick and must display the following warning or its equivalent:
WARNING
- Plastic bags can be dangerous. To avoid danger of suffocation, keep this bag away from babies and children.
MISE EN GARDE
- Les sacs de plastique peuvent être dangereux. Pour éviter le danger de suffocation, ne laissez pas ce sac à la portée des bébés ni des enfants.
Transitional Provision
180 days
18 A carriage or stroller may continue to satisfy the requirements of the Carriages and Strollers Regulations, as they read immediately before the day on which these Regulations come into force, for the period of 180 days that begins on the day of the coming into force of these Regulations.
Repeal
19 The Carriages and Strollers Regulations footnote 1 are repealed.
Coming into Force
20 These Regulations come into force on the day on which they are published in the Canada Gazette, Part II.
SCHEDULE 1
(Paragraph 4(c))
Permissible Limits of Toxicity
1 (1) For the purposes of these Regulations, a substance or stuffing material is toxic for humans in all of the following cases:
- (a) its acute oral LD50 value for rat is 5 g or less per kg of body weight;
- (b) its acute dermal LD50 value for rabbit is 2 g or less per kg of body weight;
- (c) its LC50 value for a one-hour exposure, determined using acute toxicity test results for rats, is 20,000 ppm by volume of gas or vapour or less, or 200 mg/L by volume of mist or dust or less, if gas, vapour, mist or dust is likely to be encountered when the substance or stuffing material is used in a reasonably foreseeable manner.
(2) LD50 and LC50 values are to be determined in accordance with good scientific practices.
SCHEDULE 2
(Paragraph 9(1)(b))
Standard Sans-serif Type